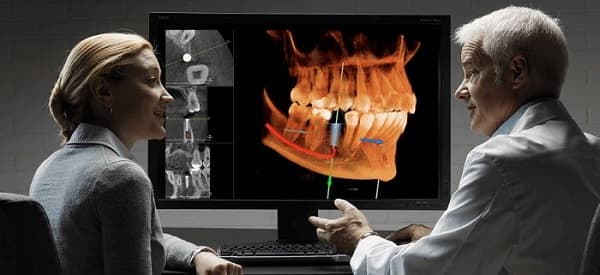
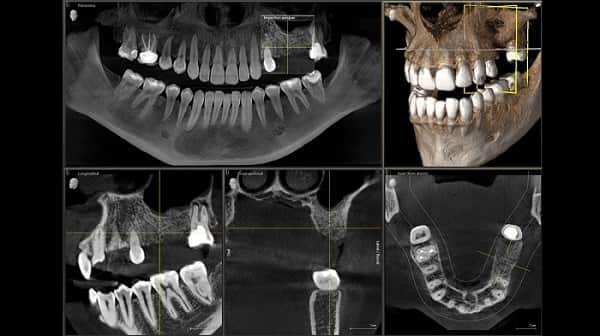
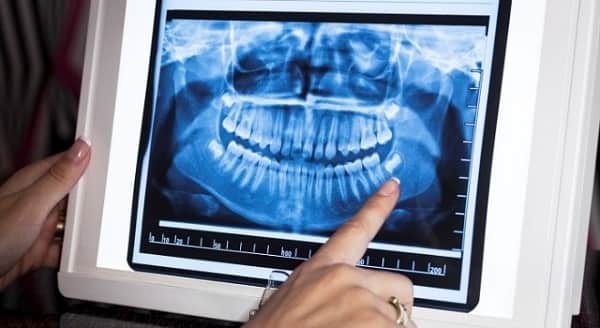
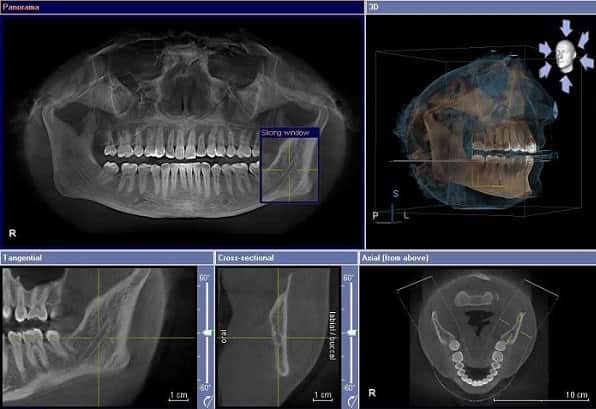
Unlike traditional x-rays, the 3-D imaging system can create either a 2-D or a 3-D image, & includes scans of your tissues in addition to bones & teeth. 3-D dental imaging is sometimes referred to as cone beam CT scanning, which is the technology that makes the scan possible. The dentist can zoom in on the scan, rotate it and view it at any angle, and even look through scans at different depths. This scan can visualize your teeth, roots, gums, bones, nerves, & airways & how all of these structures relate to each other. 3D x-rays give a better, more accurate picture of your mouth & require less radiation than traditional x-rays. These precise 3D images help dentists identify potential problems & design highly customized treatment plans to keep your teeth healthy.
What Is 3D Dentistry?
When we think about visiting the dentist’s office, we often think of bright lights, blue bibs, toothbrushes, picks, drills and bubblegum toothpaste. However, advanced imaging utilizing cone-beam computed tomography machine, also known as a CBCT machine technology is slowly but surely making its way into dental offices across the United States. Because of their wide recognition as contributors to quality dental care, CBCT machines are now becoming more commonplace among technologically up-to-date offices across the world.
3D dentistry, at its most basic, involves developing a digital, 3D image of the mouth and skull. Traditional X-rays only develop a 2D picture of your mouth, while other methods took longer bouts of radiation to create a detailed picture, and were more unpleasant and intrusive to the patient.
3D dental images are most often used for diagnosis and treatment planning. Being able to see the mouth in three dimensions allows the dentist to better and more effectively formulate an approach to treat dental conditions.
When are 3D scans used?
Dental clinics continue to use 3D dental imaging systems for a variety of clinical applications, such as dental implant planning, visualizing the progress of abnormal teeth, diagnosing root canal issues, diagnosing dental cavities, or diagnosing dental trauma. It allows dentists to get a fuller picture of the anatomical structure of the patient.
Here are some of the main ways in which scans are used in dentistry:
- Assess the quality of the jawbone where the implant will be placed.
- Determine where nerves are located.
- Diagnose tumors and disease in the early stages.
- Measure the density of the jawbone where the implant will be placed.
- Pinpoint the most effective placement for implants, including the angle of best fit.
- Plan the complete surgical procedure in advance, from start to finish.
- Precisely decide on the appropriate size and type of implants.
- View exact orientation and position of each tooth.
- View impacted teeth.
Rest assured that dentists will only use this technology when it is necessary and when it will directly benefit the patient.
What Are the Diagnostic advantages of 3D Dentistry?
The unique way 3D dentistry works means it offers numerous features found nowhere else in dental technology. This technology has a huge number of advantages over technologies like traditional X-ray and medical CT scans. The following are some of the benefits of 3D dentistry from a diagnostic standpoint:
Beam Limitation
The size of the primary X-ray beam in 3D CBCT scanners limits the radiation to only the area of interest, reducing the patient’s exposure to radiation as much as possible.
Short Scan Time
Because the CBCT scans involved in 3D dentistry can acquire all scan images in a single rotation, scan time isn’t much different from a normal scan. This reduces the chance of image defects due to the natural movement of the patient. It also minimizes time spent on the scan.
Image Accuracy
3D CBCT imaging has an incredible resolution, allowing for highly accurate imaging and measuring. This means these images can be used to pinpoint the exact location for a dental procedure.
Image Detail
With a single scan of a CBCT machine, dentists can see much more than a regular X-ray. They can see pathology, infections, nerves, musculature and so much more. This helps dentists see and properly treat dental-caused sinus issues and plan for root canals, implants and extractions. The possibilities are endless with 3D CBCT scans.
Bone Quality Assessment
3D CBCT scans can also be used to assess bone quality, which is an important part of evaluating the presence of sufficient bone for implant placement. It is also helpful in determining the size and location of lesions and breaks.
User-Friendly
3D dental equipment is very easy to learn, and it’s designed for a trained dentist or dental technician to learn and work with easily.
Interactive Display
The most important benefit for dental practitioners is the unique ability to demonstrate features in 3D that traditional imaging cannot. The practitioner can reorganize data and magnify and annotate the image.
what are the advantages of using 3D dentistry for the patient?
As it turns out, the benefits of this machinery are just as extensive for patients as they are for dentists. Some of the benefits of 3D dentistry for patients include the following:
Diagnostic Accuracy
Three-dimensional scans can catch problems 2D scans simply can’t by differentiating between many types of tissue. Pathology, infections, and abnormal sinus anatomy and joint dysfunctions can all be properly visualized and identified with 3D CBCT imaging. This means patients are properly diagnosed the first time and can get appropriate help much sooner than they would with previous methods.
Minimal Radiation Exposure
Repeated prolonged exposure to radiation can cause eye damage, the development of malignancies and other health risks, which is why new medical technologies seek to reduce patient exposure. When compared to traditional medical CT scans, 3D CBCT scans emit substantially less radiation, reducing the dosage up to 98.5%.
Non-Intrusive
No need to bite down on a mold or piece of plastic. The CBCT can scan your entire head without you needing to do anything. This is especially helpful for patients with particularly sensitive gums or teeth, as well as pediatric patients.
Short Scan Time
A typical 3D CBCT scan takes around ten seconds to complete, meaning your dentist can see and solve problems more quickly than ever.
How Does 3D Dentistry Work?
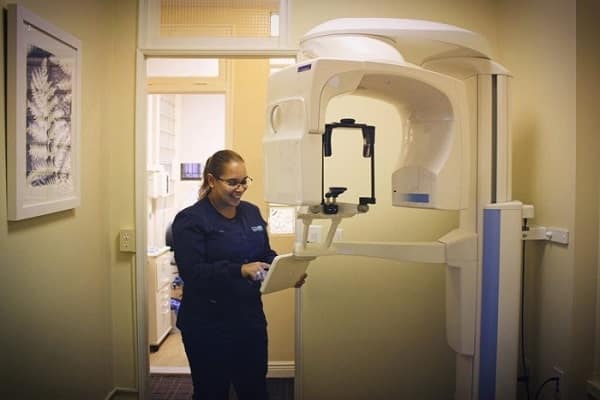
The 3D dental imaging process starts with taking a scan of the lower half of the face to create an image. The most widely recognized and technologically advanced method of completing this scan is with a cone-beam computed tomography machine, also known as a CBCT machine. This machine takes a scan of the mouth using a series of small beams of radiation, each of which produces a digital image. This series of images is formed, collected and compiled, at which point they can be converted into a three-dimensional model and used for a variety of dental purposes and procedures.
3D dentistry can be used for simple diagnostics, showing angles and features of the teeth that may not have been visible with a traditional 2D X-ray scan. However, this 3D CBCT scan can also be used to develop a complete 3D model of the skull and teeth, which can be used for complex diagnostics and comparative data. This is especially important for identifying degenerative conditions or potential problem areas down the road.
In addition to this diagnostic use, 3D dental imaging can now be integrated with digital impressions of teeth. CEREC technology allows a dentist to take digital impressions of the teeth with extreme accuracy. These digital impressions, which are used to create dental restorations, can then be merged with the 3D CBCT scan. This allows for a seamless planning of complex treatment such as dental implants, customized sleep appliances and corrective devices. This level of integration utilizing CEREC and CBCT is unmatched in the dental industry.
How Is CBCT Different From Other Methods?
The CBCT process is quite different from a medical CT scan or a traditional X-ray, primarily due to the way in which the images are collected and processed.
Medical CT scans use a fan-shaped X-ray beam that runs through the body, and they take these scans in a helical progression throughout the area of interest to develop individual slices of the image in the field of view. This may require multiple passes to get the same image a CBCT machine could get in one, making the CT scan more expensive to use and increasing the patient’s exposure to radiation.
CBCT scans also differ from the traditional dental X-ray. Instead of biting down on uncomfortable intra-oral sensors to capture the entire image of a tooth, the CBCT machine is non-intrusive, maximizing your comfort. Additionally, typical dental X-rays only focus on your teeth, and not on your entire skull or jaw. For more extensive dental surgery or implants, this is simply insufficient. Also, each traditional X-ray picture requires exposure, increasing the time between taking the X-ray and gleaning any meaningful information from it.
Preparing for the Use of 3D Technology
Make sure that you wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing on the day of your appointment, and you may also be asked to wear a gown during the procedure. Any metal objects such as jewelry, glasses, hair pins or dentures should be removed before the process begins, as these could affect the images themselves. Women should also let operator team know if there is a possibility that they are pregnant.
3D Imaging Procedure
Unlike x-rays, which are not detailed and only reveal hard tissues, Cone Beam 3D Imaging reveals the entire craniofacial structure and connective tissues. While your dentist is making plans for oral surgery or dental treatment, the images can be dissected and manipulated to ensure accuracy and precision.
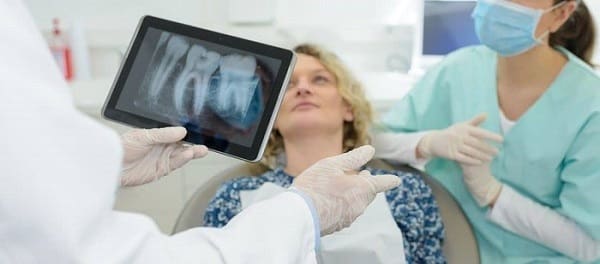
Getting a 3-D dental scan is completely painless, takes only a few minutes total. The cone beam CT scanner is mounted on an arm that rotates around your head while you stand or sit under it. You will be asked to place your chin on a special platform & the entire scanner can be raised or lowered to a height that is comfortable for you. Your only task during the scanning process is to hold as still as possible. The scan usually lasts less than half a minute.
3-D x-ray doesn’t require you to bite down on a sensor like bite-wing x-rays, but you may be asked to bite down on a small disposable tab to help ensure alignment. To get an accurate image, your face must be centered & your mouth level. A brace or strap may be used to keep your head still. The team member carrying out the scan will ensure you’re positioned properly before performing the scan.
What should I expect from 3D Imaging?
Your Cone Beam 3D Imaging experience should be quick, taking approximately 10 seconds to do a complete scan. The image produced will differ from traditional two-dimensional imaging, in that it will be a three-dimensional view of your entire head and face.
What should I expect after I’ve had a 3D scan?
Cone Beam scans are completely painless. There is no pre-scan consultation required or after care instructions.